Humans and tools
Technology allows us to shape the world around us. But at the same time our tools shape us as well. We will explore the story of human development from early prehistory with the invention of stone tools and fire till todays globalised and digitally connected world which we navigate through computers and smartphones.
The invention of new tools and technologies can be seen as crucial changing points in our history. They enabled us to interact with the world in new ways, gather new resources, build houses and shelter, communicate in new ways with each other — tools extend the abilities our bodies.
Prehistory
3 million years ago — 3,000 BCE
3.3 million years ago
Stone tools
1.5 million years ago
Fire
Ancient Age
3,000 BCE — 476 CE
5,500 years ago
Written words
5,000 years ago
Currency
Medieval Age
476 — 1492 CE
741 years ago (1280)
Mechanical Clock
571 years ago (1450)
Printing press
Modern Age
1492 — 1789 CE
413 years ago (1608)
Telescope
309 years ago (1712)
Steam engine
Contemporary Age
1789 — today
199 years ago (1822)
Computer
29 years ago (1992)
Smartphone
3.3 million years ago
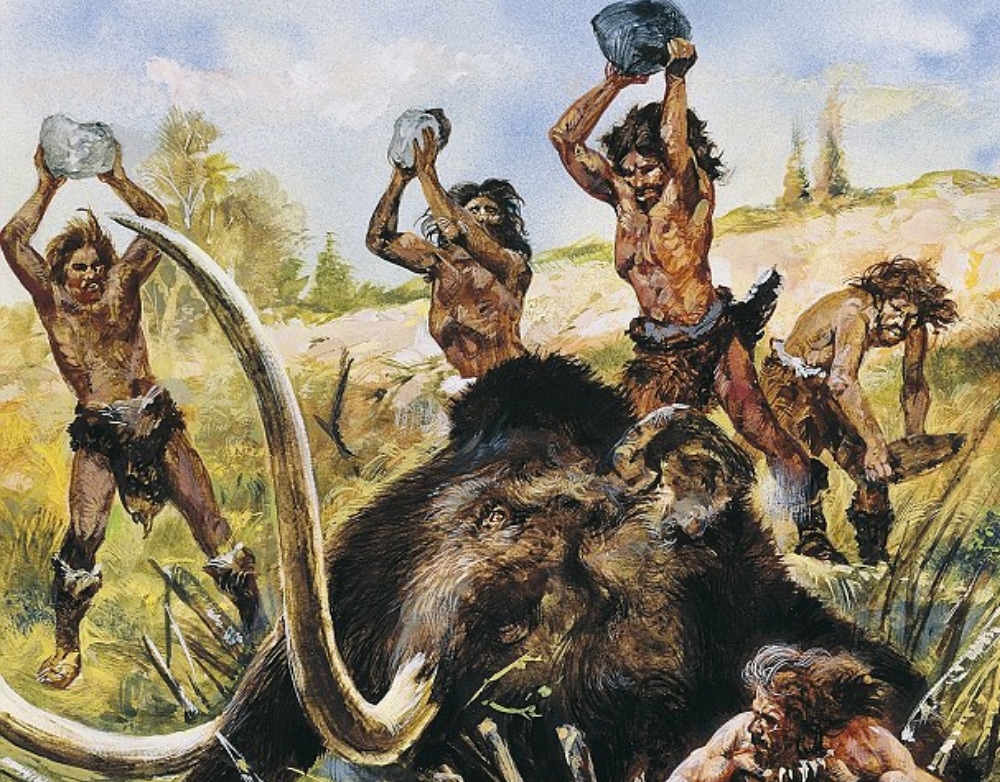


Stone
tools
The earliest stone toolmaking developed by at least 2.6 million years ago. The Early Stone Age began with the most basic stone implements made by early humans. These toolkits include hammerstones, stone cores, and sharp stone flakes. Most important is that stone tools provide evidence about the technologies, dexterity, particular kinds of mental skills ot these early human toolmakers. 1
1.5 million years ago
Fire
The control of fire by early humans was a turning point in the technological evolution of human beings. Fire provided a source of warmth and lighting, protection from predators, a way to create more advanced hunting tools, and a method for cooking food. These cultural advances allowed human geographic dispersal, cultural innovations, and changes to diet and behavior. 2
5,500 years ago
Written
words
Full writing-systems appear to have been invented independently at least four times in human history: first in Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq) where cuneiform was used between 3400 and 3300 BC, and shortly afterwards in Egypt at around 3200 BC. 3
5,500 years ago
Currency
No one knows for sure who first invented such money, but historians believe metal objects were first used as money as early as 5,000 B.C. Around 700 B.C., the Lydians became the first Western culture to make coins. Other countries and civilizations soon began to mint their own coins with specific values. 4
741 years ago (1280)
Mechanical
clock
The mechanical clock, which derived from water clock, was born in medieval Europe. The first mechanical clocks were large devices made of iron. By the fourteenth century, they were in widespread use across Europe. This innovation made it possible to produce ever smaller clocks. 5
571 years ago (1450)


Printing
press
In Germany, around 1440, goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press, which started the Printing Revolution. In Renaissance Europe, the arrival of mechanical movable type printing introduced the era of mass communication, which permanently altered the structure of society. 6
413 years ago (1608)
Telescope
The invention of the telescope played an important role in advancing our understanding of Earth's place in the cosmos. While there is evidence that the principals of telescopes were known in the late 16th century, the first telescopes were created in the Netherlands in 1608. 7
309 years ago (1712)
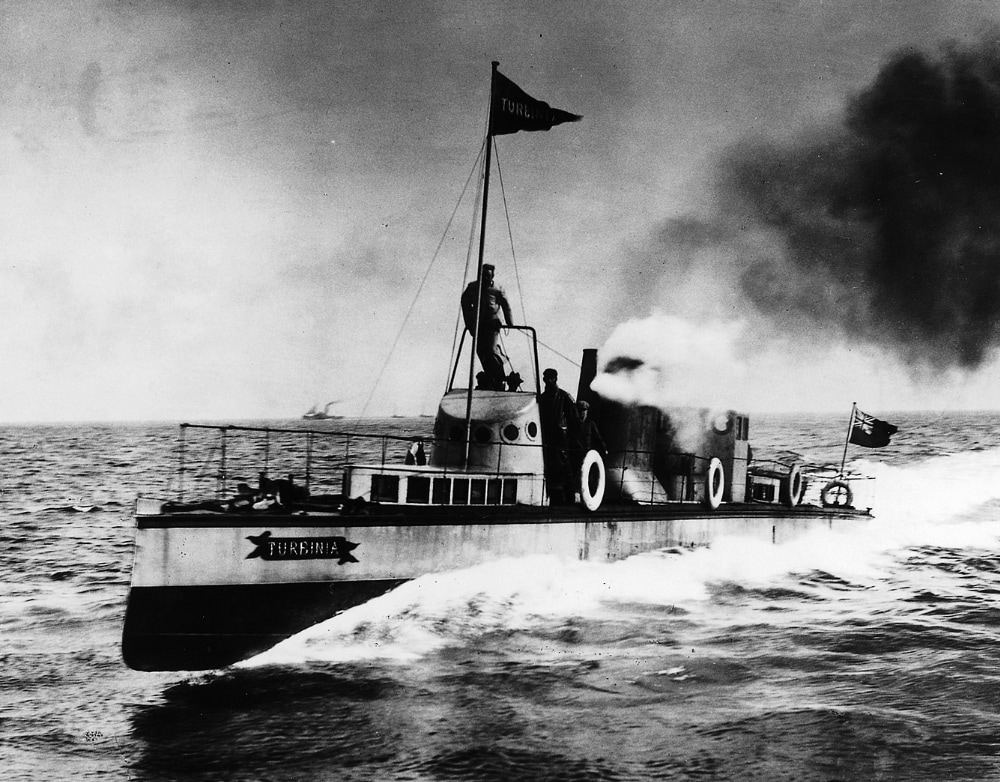

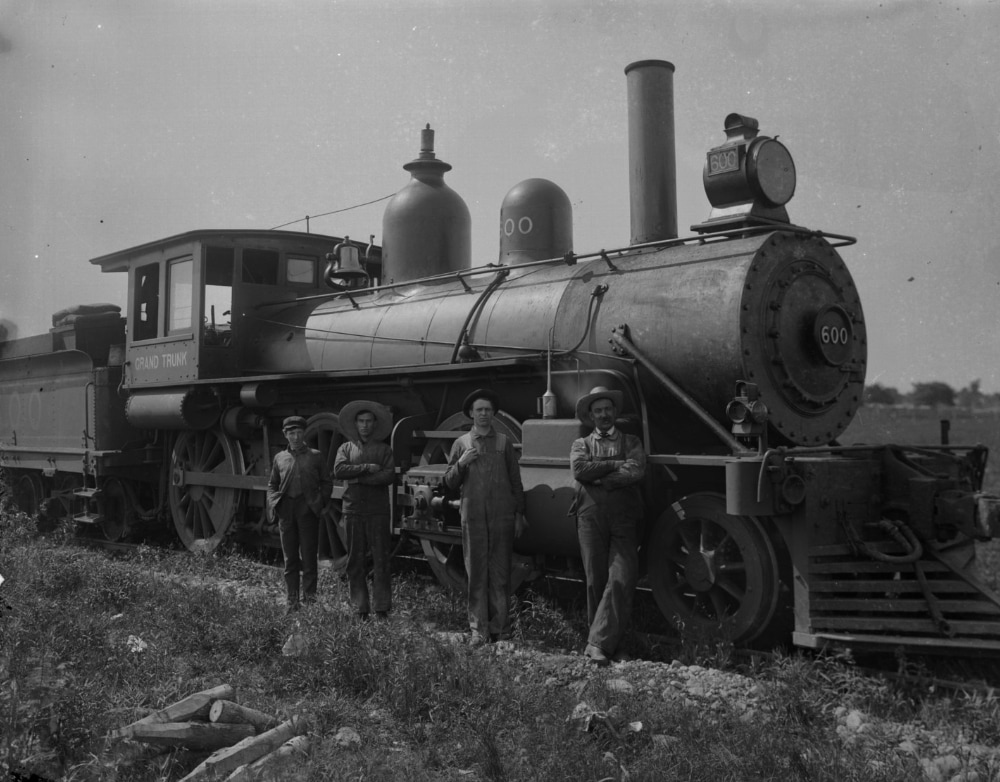
Steam
engine
During the Industrial Revolution, steam engines started to replace water and wind power, and eventually became the dominant source of power in the late 19th century and remaining so into the early decades of the 20th century, when the more efficient steam turbine and the internal combustion engine resulted in the rapid replacement of the steam engines. The steam turbine has become the most common method by which electrical power generators are driven. 8
199 years ago (1822)
Computer
Charles Babbage’s analytic engine is often seen as the forerunner of the modern computer. It had the ability to be programmed and calculate mathematical equations From these early experimental machines, we saw the development of later electronic versions. Although the electronic computer wasn’t really developed until after the 1940s. 9
Sources
Sketchfab (3D models)
sketchfab.com
Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History
Stone Tools
Wikipedia
Control of fire by early humans
Cuneiform
Printing press
History of the steam engine
Wonderopolis
Who Invented Money?
Museo Galileo
Mechanical clocks
Library of Congress
Galileo and the Telescope
Britannica
Charles Babbage
SimpleTextin
History and Evolution of Smartphones
Imprint
Concept, design & programming
Nahuel Gerth
Visual Communication
nahuelgerth.de
info@nahuelgerth.de
@nahuel.gerth
UMPRUM
Academy of Arts, Architecture and Design in Prague
náměstí Jana Palacha 80
116 93 Praha 1
Czech Republic.
©Nahuel Gerth 2021.
All rights reserved.